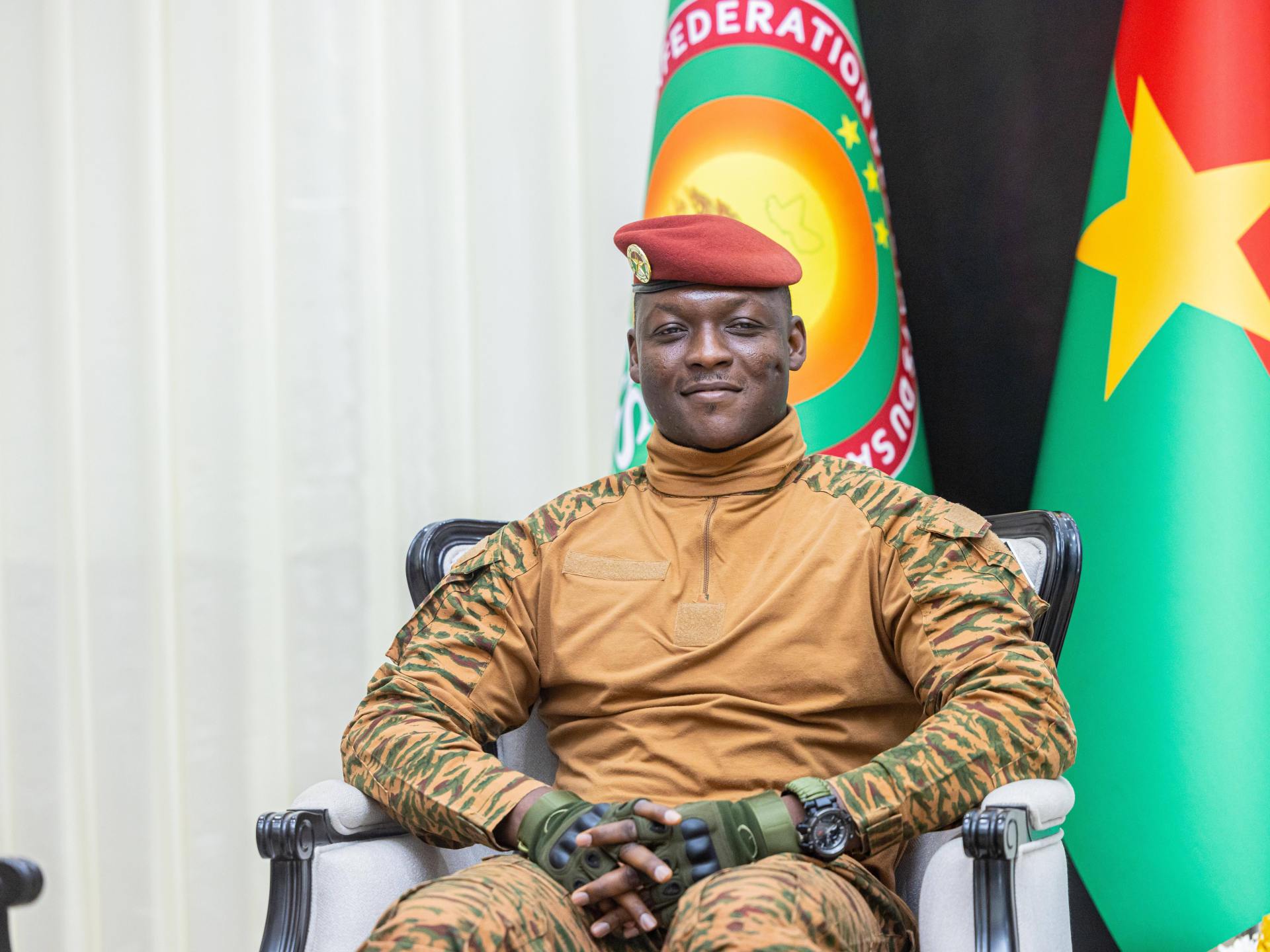
After several years of suspension, political parties in Burkina Faso have been formally dissolved by the military government, which has also seized all their assets in a move analysts say is a major blow for democracy in the West African nation.
In a decree issued on Thursday, the government, led by Captain Ibrahim Traore, scrapped all laws which established and regulated political parties, accusing them of failing to comply with guidelines.
- list 1 of 4Burkina Faso’s military government dissolves political parties
- list 2 of 4Burkina Faso leader vows AES alliance crackdown on armed groups in Sahel
- list 3 of 4Sahel summit: What is the biggest challenge facing the region?
- list 4 of 4Niger military gov’t says France, Benin, Ivory Coast behind airport attack
end of list
The troubled West African nation is struggling with violence from armed groups linked to ISIL (ISIS) and al-Qaeda. It is one of a growing number of West and Central African nations to have undergone coups in recent years.
Traore seized power in September 2022, eight months after an earlier military coup had already overthrown the democratically elected President Roch Marc Kabore.
Despite strong criticism by rights groups and opposition politicians of his authoritarian approach, 37-year-old Traore has successfully built up an online cult-like following among pan-Africanists, with many likening him to the late Burkinabe revolutionary leader, Thomas Sankara.
Traore’s anti-colonial and anti-imperial pronouncements are often shown in high-definition, AI-generated videos that have gained him widespread admiration across the internet.
But the decision to ban political parties does not sit well for democracy, Dakar-based analyst Beverly Ochieng of the Control Risks intelligence firm, told Al Jazeera.
“The military government will [remain] highly influential, especially after a recent decree appointing Traore in a supervisory capacity in the judiciary,” Ochieng said, referring to a December 2023 constitutional change which placed courts directly under government control.
Advertisement
Going forward, “there will be very limited division of powers or autonomy across the civic and political space,” Ochieng said, adding that the military government will likely keep extending its stay in power.

Why have political parties been banned?
The Burkinabe government claims the existing political parties were not following the codes which established them.
In a televised statement following a Council of Ministers meeting on Thursday, when the new decree was approved, Interior Minister Emile Zerbo said the decision was part of a broader effort to “rebuild the state” after alleged widespread abuses and dysfunction in the country’s multiparty system.
A government review, he said, had found that the multiplication of political parties had fuelled divisions and weakened social cohesion in the country.
“The government believes that the proliferation of political parties has led to excesses, fostering division among citizens and weakening the social fabric,” Zerbo said.
He did not give details of the political parties’ alleged excesses.
How did political parties operate in the past?
Before the 2022 coup, which brought the current military leadership to power, Burkina Faso had more than 100 registered political parties, with 15 represented in parliament after the 2020 general elections.
The largest was the ruling People’s Movement for Progress (MPP), which had 56 of 127 seats in parliament. It was followed by the Congress for Democracy and Progress, with 20 seats, and the New Era for Democracy with 13 seats.
But the civilian government faced months of protests as thousands took to the streets to demonstrate against growing insecurity from armed groups in large parts of the country.
In 2022, Traore took power, promising to put an end to violence by armed groups. He also promised the regional Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) bloc that his government would hold elections by 2024.
But political parties were banned from holding rallies after the 2022 coup and, a month before the 2024 deadline, Traore’s government postponed elections to 2029 after holding a national conference, which was boycotted by several political parties.
Burkina Faso, along with Mali and Niger, withdrew from ECOWAS to form the Alliance of Sahel States, a new economic and military alliance in January last year. They also withdrew from the International Criminal Court (ICC).
Advertisement
In July 2025, Traore’s government dissolved the Independent National Electoral Commission, saying the agency was too expensive.

Has insecurity worsened under Traore?
Landlocked Burkina Faso is currently grappling with several armed groups which have seized control of land in the country’s north, south and west, amounting to about 60 percent of the country, according to the Africa Center for Strategic Studies (ACSS).
The most active groups are the al-Qaeda-backed Jama’at Nusrat al-Islam wal-Muslimin (JNIM) and Islamic State Sahel Province (ISSP), which also operate in neighbouring Mali and Niger.
The groups want to rule over territory according to strict Islamic laws and are opposed to secularism.

By December 2024, all three Alliance of Sahel States countries had cut ties with former colonial power France and instead turned to Russian fighters for security support after accusing Paris of overly meddling in their countries.
Between them, they expelled more than 5,000 French soldiers who had previously provided support in the fight against armed groups. A smaller contingent of about 2,000 Russian security personnel is now stationed across the three countries.
But violence in Burkina Faso and the larger Sahel region has worsened.
Fatalities have tripled in the three years since Traore took power to reach 17,775 – mostly civilians – by last May, compared with the three years prior, when combined recorded deaths were 6,630, the ACSS recorded.
In September, Human Rights Watch accused JNIM and ISSP of massacring civilians in northern Djibo, Gorom Gorom and other towns, and of causing the displacement of tens of thousands since 2016.
HRW has also similarly accused the Burkinabe military and an allied militia group, Volunteers for the Defense of the Homeland, of atrocities against civilians suspected of cooperating with armed groups. In attacks on northern Nondin and Soro villages in early 2024, the military killed 223 civilians, including 56 babies and children, HRW said in an April 2024 report.
Mali and Niger have similarly recorded attacks by the armed groups. Malian capital Bamako has been sealed off from fuel supplies by JNIM fighters for months.
On Wednesday night, the Nigerien military held off heavy attacks on the airport in the capital city, Niamey. No armed group has yet claimed responsibility.
Is the civic space shrinking in Burkina Faso?
Since it took power, the government in Ouagadougou has been accused by rights groups of cracking down on dissent and restricting press and civic freedoms.
All political activities were first suspended immediately after the coup.
Advertisement
In April 2024, the government also took aim at the media, ordering internet service providers to suspend access to the websites and other digital platforms of the BBC, Voice of America and HRW.
Meanwhile, authorities have forced dozens of government critics into military service and sent them to fight against armed groups. Several prominent journalists and judges have been arrested after speaking out against increasingly restrictive rules on press and judiciary freedom.
Abdoul Gafarou Nacro, a deputy prosecutor at the country’s High Court, was one of at least five senior members of the judiciary to be forcibly conscripted and sent to fight armed groups in August 2024 after speaking out against the military government. Nacro’s whereabouts are currently unknown.
In April 2025, three abducted journalists resurfaced in a social media video 10 days after they went missing, in one example. All three – Guezouma Sanogo, Boukari Ouoba, and Luc Pagbelguem – were wearing military fatigues in an apparent forced conscription. They have all since been released.
However, several others, including some opposition politicians, are still missing.
Related News

Ecuador announces 30 percent tariff on Colombia over drug trafficking

North Korea’s Kim Jong Un fires vice premier, publicly rebukes officials

US dollar: ‘Wounded hegemon’ or secure as most powerful currency on earth?